Peripheral Arterial Disease Diagnosis & Treatment
City skyline
ButtonAt Eastlake Cardiovascular, several of our physicians specialize in the diagnosis and treatment of peripheral arterial disease.
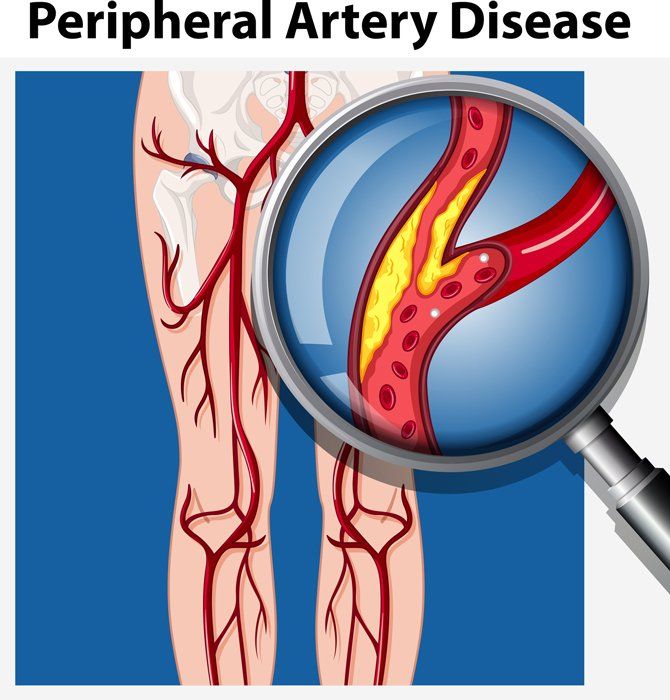
Peripheral Artery Disease (PAD) is a condition that develops when the arteries that carry blood from the heart around our body become clogged with plaque. We most often are referring to the arteries of the legs, but it may also include the carotid arteries that deliver blood to the brain, and renal arteries that deliver blood to the kidneys. Plaque is made up of cholesterol and fat, which can occlude or slow the circulation. Our muscles, tissue and organs rely on the delivery of oxygen and nutrients to work properly. Devastating consequences can occur when the arterial circulation becomes diseased, or obstructed. Maintaining healthy arteries is important in preventing not only heart attacks, but also to decrease the risk of stroke, amputation, and loss of muscle strength and ability that is seen with PAD.
WHAT ARE MY RISKS FOR GETTING PAD?
The risk factors for developing PAD are similar to those for coronary artery or heart disease. However, if you have a history of smoking or have diabetes your risk increases dramatically. As we age, our arteries may also become blocked through this process of plaque buildup or, atherosclerosis. It is important to speak with your healthcare provider about your risk. Having even “borderline” diabetes or if you’ve quit smoking still places you at a higher chance of developing PAD. Some people may not even know they have diabetes until a special blood test is checked. Other risk factors for developing PAD are high blood pressure, high cholesterol, heart disease, obesity, sedentary life style, and kidney disease.
WHAT ARE THE SIGNS OF PAD?
Claudication occurs when there is not sufficient blood flow to an exercising leg muscles. It is often described as an aching, cramping, heaviness or even a generalized weakness in the muscles of the legs. It is brought on by activity and relieved within 5-10 minutes of rest. Someone suffering from claudication may need to walk slower, have trouble keeping up with others, and/or may need a cane or walker. Symptoms can be very subtle. Rest pain is a symptom of advanced PAD. It is typically described as a burning, cramping pain in the ball of the foot and toes that is worse at night while in bed. Someone suffering from rest pain will often need to dangle their legs over the side of the bed or sleep in a recliner to gain gravity assisted blood flow and relieve the pain. They may also get up frequently through the night to “walk off the pain or cramp,” or use pain medication. Rest pain will occur on a consistent basis most nights of the week. The risk for developing an ulcer or sore which can lead to gangrene or even amputation is quite high with more advanced PAD. PAD is often associated with color changes in the skin, loss of feeling and coldness. Skin may be pale or dark purple or black areas may develop on the toes. Sores can form easily and will have a difficult time healing. Your pulses may also be faint or even absent. If you feel you are less active due to claudication or have diminished muscle strength or balance in your legs you should speak with your physician about your risk for PAD. To avoid symptoms, people will walk slower or avoid activities that require walking. The vague complaints often seen with PAD may be mistaken for old age, debility or even arthritis. Today there are treatment options to improve function and restore quality of life.